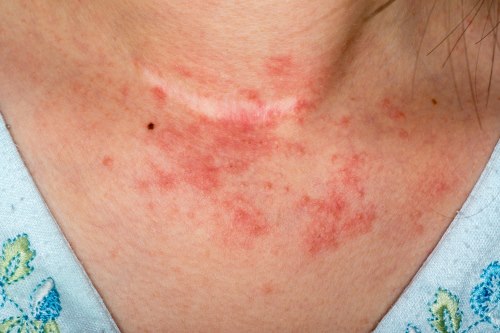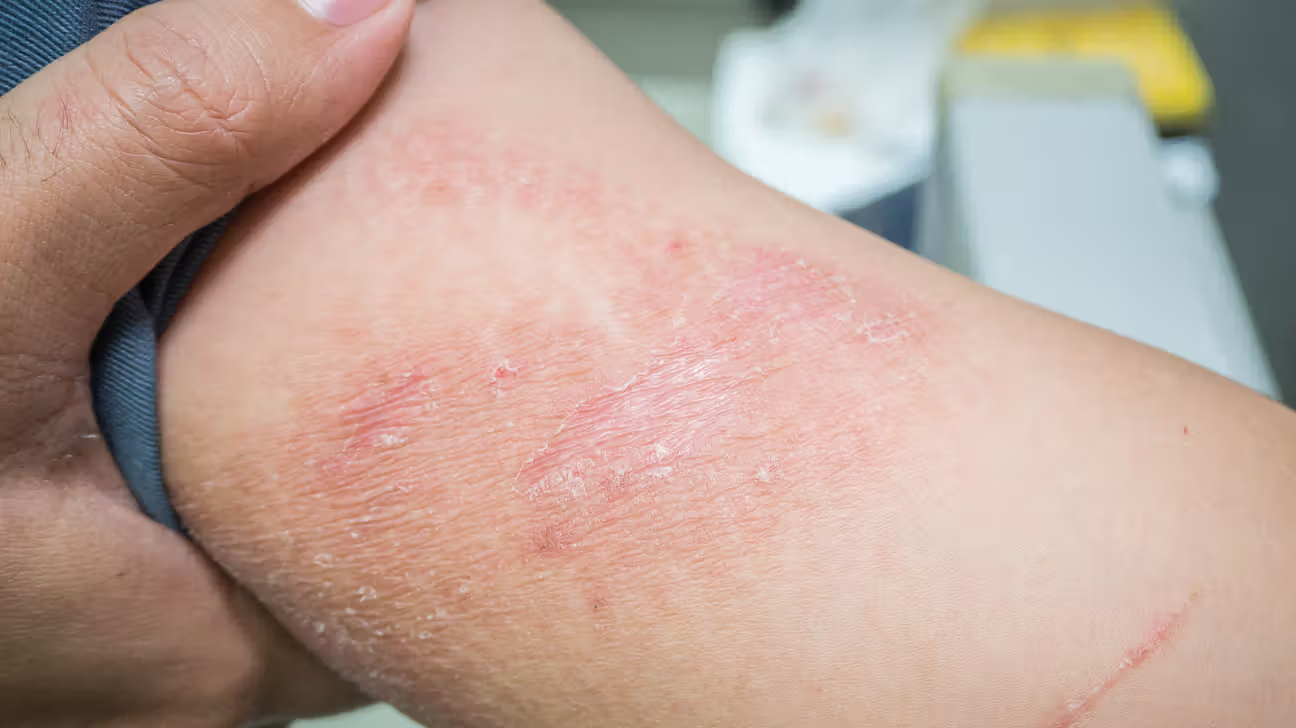
Dermatitis is a general term for inflammation of the skin, which can result in redness, itching, swelling, and sometimes blistering or scaling. There are different types of dermatitis, such as atopic dermatitis (eczema), contact dermatitis, seborrheic dermatitis, and others. Treatment focuses on reducing inflammation, relieving symptoms, and preventing flare-ups.
Dermatitis Treatment Options
1. Topical Treatments
- Corticosteroid Creams or Ointments : These help reduce inflammation and itching. Mild corticosteroids are available over the counter, while stronger formulations require a prescription.
- Topical Calcineurin Inhibitors (e.g., Tacrolimus, Pimecrolimus) : Used to treat eczema and other types of dermatitis, especially for sensitive areas like the face.
- Moisturizers and Emollients : Help hydrate the skin and create a protective barrier to reduce dryness and irritation. Use them regularly, even when symptoms are not present.
2. Oral Medications
- Antihistamines : Can help reduce itching and discomfort, especially if itching affects sleep. Common options include diphenhydramine or cetirizine.
- Oral Corticosteroids : In cases of severe dermatitis, a short course of oral corticosteroids may be prescribed to reduce inflammation.
- Immunosuppressants : For chronic or severe cases, medications like cyclosporine or methotrexate may be used under medical supervision.
3. Light Therapy (Phototherapy)
- Ultraviolet (UV) Light Therapy : Can be beneficial for certain types of dermatitis, especially atopic dermatitis (eczema) that does not respond to topical treatments.
4. Home Remedies and Lifestyle Changes
- Avoid Triggers : Identify and avoid substances that can worsen dermatitis, such as certain soaps, cosmetics, or allergens.
- Use Gentle Cleansers : Opt for soap-free cleansers and avoid hot water, which can dry out the skin.
- Wear Loose-Fitting Clothing : Choose breathable fabrics like cotton to reduce irritation.
5. Treatment for Specific Types of Dermatitis
- Atopic Dermatitis (Eczema) : Use moisturizers regularly and avoid known triggers (e.g., certain foods, allergens). Topical corticosteroids may be prescribed for flare-ups.
- Contact Dermatitis : Identify and avoid the irritant or allergen causing the reaction. Corticosteroid creams can help reduce inflammation.
- Seborrheic Dermatitis : Use medicated shampoos containing ketoconazole, selenium sulfide, or zinc pyrithione for scalp involvement. Topical antifungals and corticosteroids can be used for other affected areas.
6. Preventive Care
- Moisturize Regularly : Apply a fragrance-free moisturizer daily to keep the skin hydrated and prevent dryness.
- Manage Stress : Since stress can trigger or worsen dermatitis, practicing stress-reducing techniques like meditation, yoga, or regular exercise may help.
Dermatitis Treatment F&Q
Dermatitis is an inflammation of the skin characterized by redness, itching, and swelling. Common types include atopic dermatitis (eczema), contact dermatitis, and seborrheic dermatitis.
Dermatitis can be triggered by various factors, including allergens (like pollen or certain foods), irritants (such as soaps or chemicals), genetics, stress, and environmental factors.
Symptoms typically include red, inflamed skin, itching, dryness, flaking, and sometimes blistering or oozing. The severity and appearance can vary depending on the type of dermatitis.
A healthcare provider will perform a physical examination and review your medical history. In some cases, patch testing or allergy tests may be recommended to identify triggers.
Treatments often include topical corticosteroids, calcineurin inhibitors, moisturizers, antihistamines, and in severe cases, oral corticosteroids or immunosuppressants. Light therapy may also be beneficial.
While there is no definitive cure for chronic types of dermatitis, effective management can reduce symptoms and prevent flare-ups. Many people can achieve significant improvement with appropriate treatment.